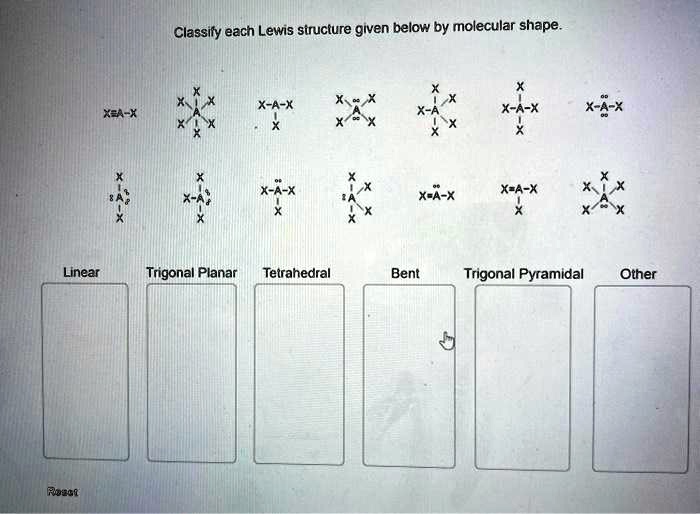
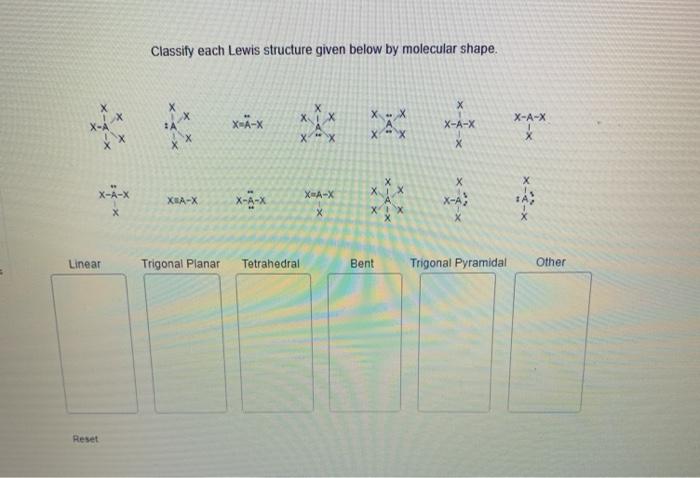
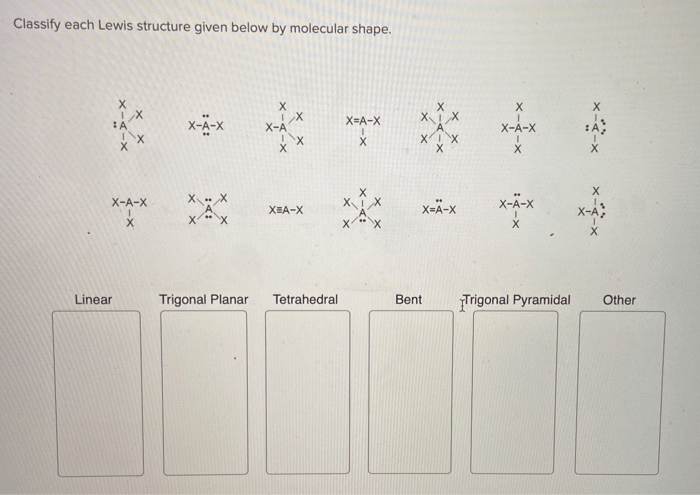
Classify each lewis structure given below by molecular shape – Introducing the captivating realm of molecular shape classification, where the intricate dance of electrons orchestrates the geometry of molecules. By delving into the secrets of Lewis structures, we unlock the key to unraveling the molecular architecture that underpins the behavior and properties of matter.
This discourse will embark on a journey to classify molecular shapes, deciphering the relationship between electron pair geometry and molecular shape. Through examples and in-depth analysis, we will illuminate the exceptions to the VSEPR theory, revealing the fascinating nuances that shape our understanding of molecular structures.
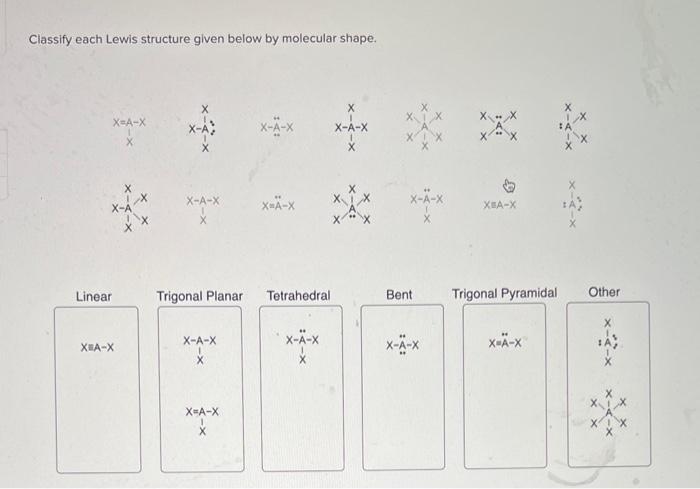
Identify Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule. They show the arrangement of electrons in the valence shells of the atoms and the covalent bonds that form between them.
To draw a Lewis structure, first determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. Then, arrange the atoms in a way that minimizes the number of unpaired electrons. Finally, connect the atoms with covalent bonds, making sure that each atom has a complete valence shell.
Lewis structures are important because they can help us to understand the properties of molecules. For example, the shape of a molecule can be predicted from its Lewis structure. Lewis structures can also be used to determine the polarity of a molecule and its reactivity.
Classify Molecular Shapes
The shape of a molecule is determined by the arrangement of its atoms and the number of electron pairs around each atom. The electron pair geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of the electron pairs around each atom, including both bonding and non-bonding electron pairs.
The following table shows the different molecular shapes and their corresponding electron pair geometries:
| Molecular Shape | Electron Pair Geometry |
|---|---|
| Linear | 2 |
| Trigonal planar | 3 |
| Tetrahedral | 4 |
| Trigonal pyramidal | 3 + 1 |
| Bent | 2 + 1 |
| T-shaped | 3 + 2 |
| Square planar | 4 + 0 |
| Octahedral | 6 |
The relationship between electron pair geometry and molecular shape is that the molecular shape is determined by the electron pair geometry of the central atom in the molecule.
Analyze Lewis Structures for Molecular Shape
To analyze a Lewis structure for molecular shape, first determine the electron pair geometry of each atom in the molecule. Then, use the table above to determine the molecular shape.
The following table shows some examples of Lewis structures and their corresponding molecular shapes:
| Lewis Structure | Electron Pair Geometry | Molecular Shape |
|---|---|---|
H-H |
2 | Linear |
H-C-H |
3 | Trigonal planar |
H-C-HH |
4 | Tetrahedral |
H-N-H |
3 + 1 | Trigonal pyramidal |
H-O-H |
2 + 1 | Bent |
H-C-HCl |
3 + 2 | T-shaped |
Cl-C-Cl |
4 + 0 | Square planar |
H-C-HHH |
6 | Octahedral |
The steps involved in analyzing Lewis structures for molecular shape are as follows:
- Draw the Lewis structure of the molecule.
- Determine the electron pair geometry of each atom in the molecule.
- Use the table above to determine the molecular shape.
Exceptions to Molecular Shape Classifications: Classify Each Lewis Structure Given Below By Molecular Shape
There are some exceptions to the VSEPR theory, which predicts the molecular shape based on the electron pair geometry. These exceptions occur when there are lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. Lone pairs of electrons can repel other electron pairs, which can cause the molecular shape to deviate from the predicted shape.
For example, the molecule SF 4has a tetrahedral electron pair geometry, but its molecular shape is square pyramidal. This is because the lone pair of electrons on the sulfur atom repels the bonding electron pairs, which causes the molecule to adopt a square pyramidal shape.
Another example is the molecule XeF 4, which has a square planar electron pair geometry, but its molecular shape is distorted. This is because the lone pair of electrons on the xenon atom repels the bonding electron pairs, which causes the molecule to adopt a distorted square planar shape.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the VSEPR theory?
The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory predicts the molecular shape based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom.
How do you determine the molecular shape from a Lewis structure?
By identifying the number of electron pairs around the central atom and applying the VSEPR theory, you can predict the molecular shape.
What are the exceptions to the VSEPR theory?
Molecules with lone pairs on the central atom or those involving resonance may exhibit deviations from the predicted VSEPR shapes.