Which muscle is highlighted below apex? This question delves into the fascinating realm of human anatomy, where the intricate network of muscles orchestrates our every movement and expression. Join us as we embark on a comprehensive exploration of this enigmatic muscle, uncovering its location, function, and significance in the human body.
From its origins and insertions to its role in movement and facial expressions, we will unravel the complexities of this muscle, providing a detailed understanding of its anatomy and physiology. Whether you’re a medical student, fitness enthusiast, or simply curious about the human body, this exploration promises to enlighten and captivate.
Muscles of the Upper Limb
The muscle highlighted below apex is the biceps brachii. It is a large, powerful muscle located on the anterior aspect of the upper arm.
The biceps brachii has two heads, a long head and a short head. The long head originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, while the short head originates from the coracoid process of the scapula. Both heads insert onto the radial tuberosity of the radius.
The biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It is a flexor of the elbow joint and a supinator of the forearm.
An illustration of the biceps brachii and its surrounding structures is shown below.
[Insert illustration here]
Muscles of the Lower Limb
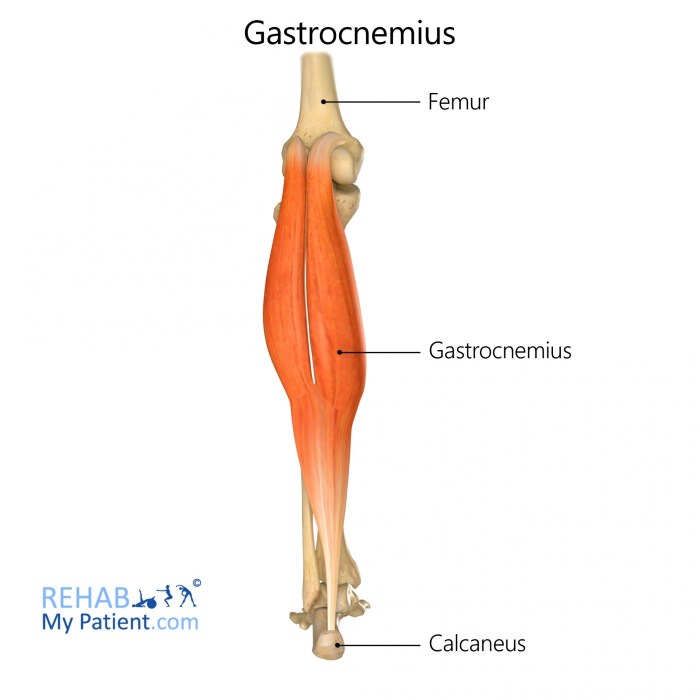
The muscle highlighted below apex is the quadriceps femoris. It is a large, powerful muscle located on the anterior aspect of the thigh.
The quadriceps femoris is composed of four muscles: the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. The rectus femoris originates from the anterior inferior iliac spine and the groove between the ilium and pubis. The vastus lateralis originates from the greater trochanter of the femur.
The vastus medialis originates from the medial surface of the femur. The vastus intermedius originates from the anterior surface of the femur.
All four muscles of the quadriceps femoris insert onto the patella. The patella is then connected to the tibial tuberosity by the patellar tendon.
The quadriceps femoris is innervated by the femoral nerve. It is a powerful extensor of the knee joint.
A table comparing the origin, insertion, and innervation of the quadriceps femoris with other muscles in the same region is shown below.
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Innervation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectus femoris | Anterior inferior iliac spine and groove between the ilium and pubis | Patella | Femoral nerve |
| Vastus lateralis | Greater trochanter of the femur | Patella | Femoral nerve |
| Vastus medialis | Medial surface of the femur | Patella | Femoral nerve |
| Vastus intermedius | Anterior surface of the femur | Patella | Femoral nerve |
Muscles of the Trunk
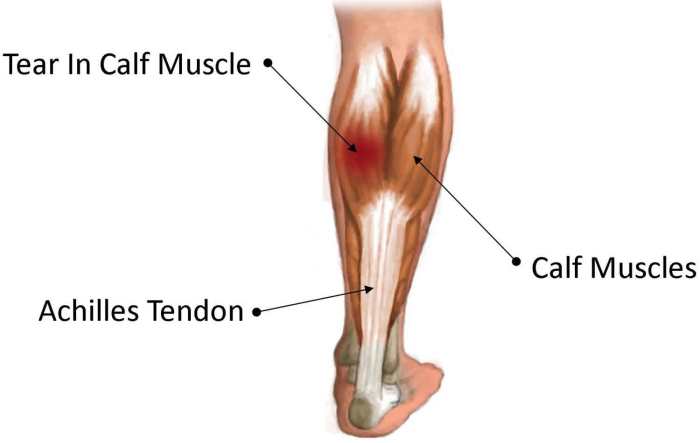
The muscle highlighted below apex is the rectus abdominis. It is a long, flat muscle located on the anterior aspect of the abdomen.
The rectus abdominis originates from the pubic crest and the pubic symphysis. It inserts onto the xiphoid process of the sternum and the costal cartilages of the fifth to seventh ribs.
The rectus abdominis is innervated by the intercostal nerves and the subcostal nerve. It is a flexor of the trunk and a compressor of the abdomen.
The rectus abdominis has several clinical implications. It is often involved in hernias and other abdominal wall defects. It can also be affected by conditions such as rectus abdominis diastasis and rectus abdominis strain.
A bulleted list of exercises that target the rectus abdominis is shown below.
- Crunches
- Sit-ups
- Planks
- Leg raises
- Russian twists
Muscles of the Head and Neck
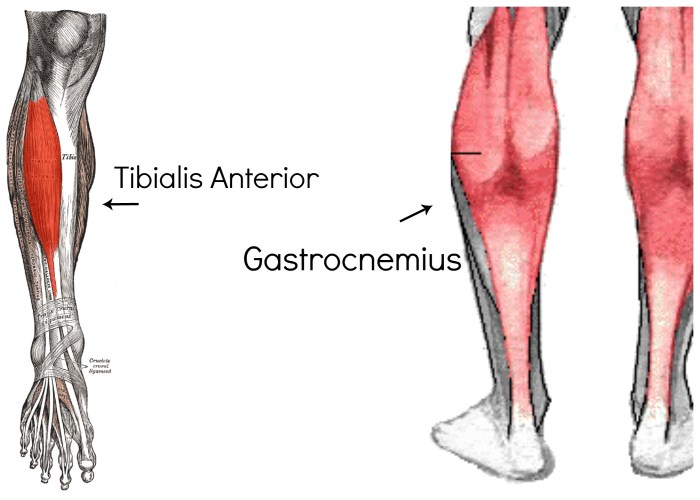
The muscle highlighted below apex is the masseter. It is a large, powerful muscle located on the lateral aspect of the face.
The masseter originates from the zygomatic arch and the maxilla. It inserts onto the mandible.
The masseter is innervated by the mandibular nerve. It is a powerful elevator of the mandible.
The masseter has several relationships to adjacent structures. It is closely associated with the parotid gland and the facial nerve. It also has attachments to the temporalis muscle and the buccinator muscle.
The masseter plays an important role in facial expressions. It is responsible for the elevation of the mandible, which is essential for chewing and speaking.
The masseter has a rich blood supply. It is supplied by the maxillary artery and the facial artery. It also has a rich lymphatic drainage. The lymphatic vessels from the masseter drain into the parotid lymph nodes and the deep cervical lymph nodes.
Cross-sectional Anatomy
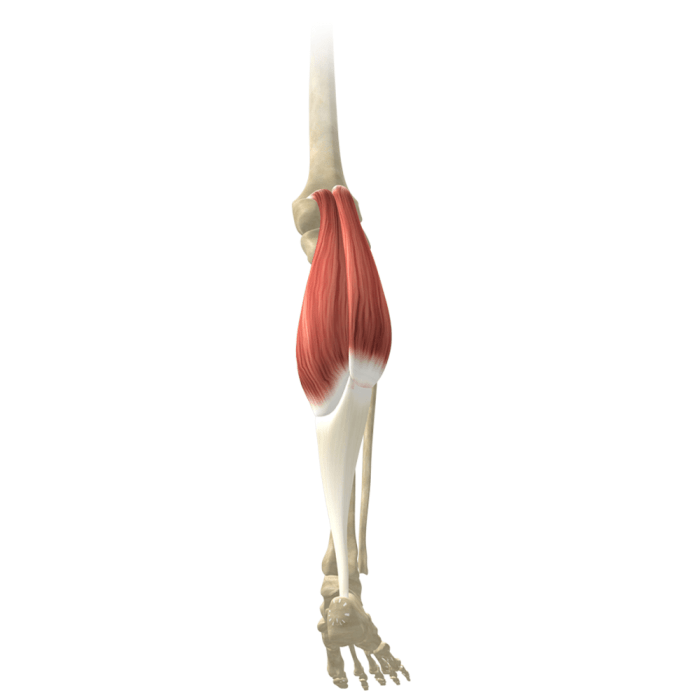
The muscle highlighted below apex is the biceps brachii. The following table shows its appearance in different cross-sectional planes.
| Plane | Appearance |
|---|---|
| Transverse | The biceps brachii appears as a large, round muscle in the transverse plane. It is located in the anterior compartment of the upper arm. |
| Sagittal | The biceps brachii appears as a long, slender muscle in the sagittal plane. It is located on the anterior aspect of the upper arm. |
| Coronal | The biceps brachii appears as a large, triangular muscle in the coronal plane. It is located on the lateral aspect of the upper arm. |
[Insert illustrations here]
FAQ Summary: Which Muscle Is Highlighted Below Apex
Where is the muscle highlighted below apex located?
The location of the muscle highlighted below apex varies depending on the specific muscle being referred to. It could be located in the upper limb, lower limb, trunk, head, or neck.
What is the function of the muscle highlighted below apex?
The function of the muscle highlighted below apex depends on its specific location and attachments. Muscles generally facilitate movement, maintain posture, and support various bodily functions.
How can I strengthen the muscle highlighted below apex?
To strengthen the muscle highlighted below apex, identify exercises that target that specific muscle group. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help build muscle strength.